Transferring Files Between WSL and Windows
Logging into Zomro VPS using WSL in Ubuntu CLI
To log into your Zomro VPS using WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) in the Ubuntu CLI, you can use the ssh command. Here are the steps to do it:
- Open your Ubuntu terminal in WSL. You can do this by searching for "Ubuntu" in the Windows Start menu and launching it.
- In the Ubuntu terminal, use the
sshcommand to connect to your Zomro VPS. Replaceyour_usernamewith your actual username andyour_server_ipwith the IP address of your Zomro VPS:
ssh your_username@your_server_ip
For example, if your username is "root" and your server's IP address is "123.456.789.0," the command would be:
ssh root@123.456.789.0
- Press Enter after entering the command. You will be prompted to enter your password for the VPS.
- After entering the correct password, you should be logged into your Zomro VPS via SSH. You will see a command prompt for your VPS, and you can start running commands on the remote server.
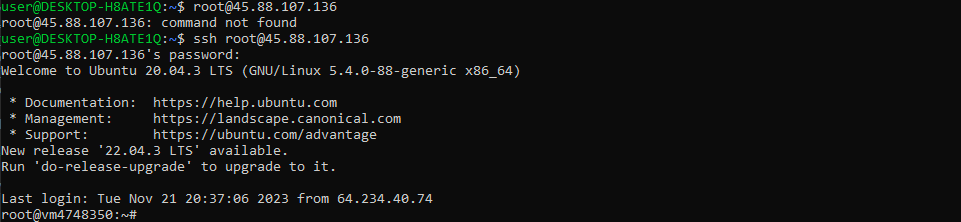
That's it! You have successfully logged into your Zomro VPS using WSL's Ubuntu CLI. You can now manage your server and perform various tasks as needed.
Locating File Paths in Ubuntu CLI
In Ubuntu CLI (Command Line Interface), it's essential to know how to find the file paths of directories and files. This knowledge allows you to navigate your file system effectively and reference files for various tasks. Here are some useful commands and techniques for locating file paths:
Present Working Directory (pwd)
The pwd command stands for "Present Working Directory" and displays the absolute path of your current location within the file system. Simply enter the following command:
pwd
The terminal will respond with the absolute path to your current directory, helping you understand where you are in the file system.
Listing Directory Contents (ls)
The ls command is used to list the contents of a directory. When executed without any arguments, it displays the files and subdirectories in your current directory. For example:
ls
This command will list the files and directories in your current location.
Finding a File (find)
If you need to locate a specific file within your file system, you can use the find command. Specify the starting directory and the filename you're looking for. For example, to find a file named "example.txt" starting from the root directory, use:
find / -name example.txt
This command will search the entire file system for "example.txt" and display its path if found.
Navigating Directories (cd)
The cd command allows you to change directories and move through the file system. You can use it to navigate to specific locations. For instance, to move to a directory named "documents," use:
cd documents
You can also use relative paths, such as cd .. to go up one level or cd /path/to/directory to specify an absolute path.
File Explorer Integration
In many cases, you can easily locate file paths by using a graphical file explorer like Windows File Explorer. WSL allows you to access your Windows files and directories under the /mnt directory. For example, your Windows C: drive is typically accessible at /mnt/c/.
Understanding how to locate file paths in Ubuntu CLI is crucial for efficient file management and navigation. These commands and techniques will empower you to work effectively with your files and directories.
Transferring Files from WSL to Windows
Transferring files from your WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) environment to your Windows system is a common task and can be done using several methods. I’ll be discussing the Secure Copy method in this tutorial.
Using SCP (Secure Copy)
You can transfer files from WSL using the scp (Secure Copy) command. Here's the syntax:
scp username@WindowsIP:/path/to/source/file /path/to/destination/in/WSL/
username: Your Windows username.WindowsIP: The IP address or hostname of your Windows system./path/to/source/file: The path to the file in your Windows file system that you want to copy./path/to/destination/in/WSL/: The destination path in your WSL environment.
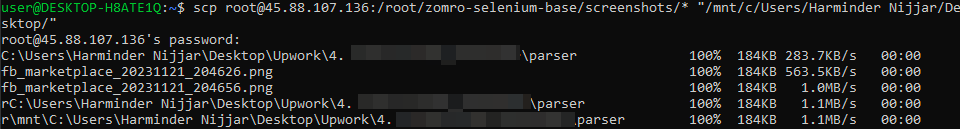
For example, to copy all files located in /root/zomro-selenium-base/screenshots/* to your Windows Desktop, you can use:
scp root@45.88.107.136:/root/zomro-selenium-base/screenshots/* "/mnt/c/Users/Harminder Nijjar/Desktop/"
This command will copy all files in /root/zomro-selenium-base/screenshots/ to your Windows Desktop. Make sure to adjust the source and destination paths as needed for your specific use case.
Conclusion
Transferring files between WSL and Windows is a common operation and can be accomplished using the Secure Copy (SCP) command. Whether you need to copy files from WSL to Windows or from Windows to WSL, SCP provides a secure and efficient